Matter is everything around us. Atom and compounds are made of every small parts of matter
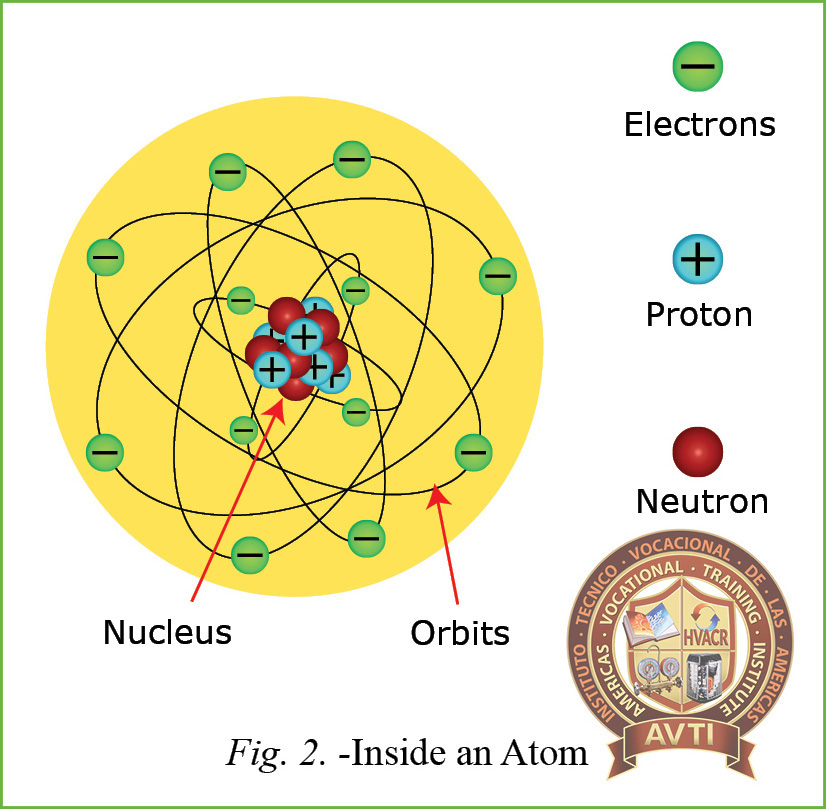
Atoms are composed of three parts:
- Protons are founding the nucleus of the atom and it has a positive (+) electrical charge
- Electrons they orbit the nucleus of the atom and they have a negative (-) electrical charge.
- Neutrons found in the nucleus of the atom and has no electrical charge and has no effect on the electrical characteristic of the materials.
Electrical energy is released when electrons move from one atom to another. Atoms try to maintain equal numbers between positive (+) and negative (-) charges (protons vs. elec- trons). An atom having lost an electron becomes positively charged (+), due to the excess proton. An atom having an extra electron becomes negatively charged (-).
One of the simplest atoms is the hydrogen atom; it contains one proton and one electron. The proton has a positive charge (+) that equally balances the negative charge (-) of electron.
Other elements have more than one proton and one electron in their atoms. All electrons pos- sess the same negative charge, while all protons posses an equal positive charge. Their charges are equal an opposite; hence, they neutralize each other. Any stable or electrically balanced atom has an equal number of protons and electrons.
A stable atom is said to have a neutral charge. An atom can have from 1 to over 100 elec- trons, depending on the element. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8; therefore, it has 8 elec- trons orbiting around the nucleus. Copper has an atomic number of 29, so it has 29 electrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus much like the planets orbit around the sun. Electrons travel in pathways called shells. Electrons traveling in shells located close to the nucleus are more tightly bound to the nucleus than those in the outer shells. The outer shell can hold no more than eight electrons. Electrons located in the outer shell are called free, orbital, plan- etary, or valance electrons.