Electricity is a form of energy, in which electrons move from one atom to another atom. Therefore, electricity is the flow of electrons. Other forms of energy are: heat, light, chemical (battery), atomic (power plant), and mechanical (motor). Energy cannot be destroyed, but can be converted from one form of energy to another. For example, heat is used to produce electricity which can be used to produce light.
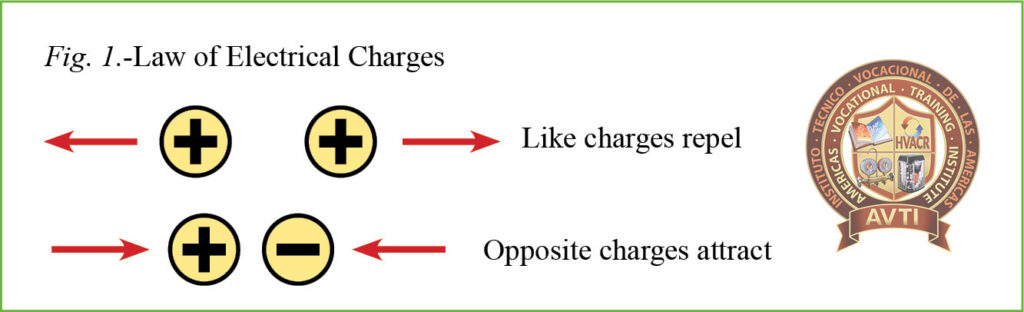
Electrical energy is the movement of electrons through a conductor. Electrical appliances are designed to convert electrical energy to other forms of energy, and thus perform useful work. Some devices produce heat while other devices produce motion or light, defining them as an electrical load which is anything that does useful work such as heat, light and magnetism. The Law of Electric Charges states: like charges repel and opposites attract. Excess electrons are attracted to atoms lacking electrons. To perform useful work, a constant and steady movement of electrons must be produced.